Organizing web content effectively is a critical skill for web developers, content creators, and business owners alike. A well-structured website enhances user experience, boosts SEO performance, and increases the likelihood of achieving your site’s goals, whether those are sales, lead generation, or simply sharing valuable information.
This tutorial is designed to guide you through the nuances of organizing web content, catering to all levels of expertise. Whether you’re a beginner creating your first website or a seasoned professional looking to refine your strategies, these steps will ensure your content is clear, accessible, and optimized for success.
Why Organizing Web Content Matters
Before diving into the “how,” it’s crucial to understand the “why.” Properly organized web content:
- Improves User Experience (UX): Visitors can quickly find the information they need, reducing frustration and increasing satisfaction.
- Boosts SEO Rankings: Search engines prioritize websites that are easy to navigate and provide clear, structured information.
- Enhances Accessibility: Structured content ensures accessibility for all users, including those relying on screen readers.
- Increases Engagement: Logical layouts and navigation paths encourage users to explore more pages, lowering bounce rates.
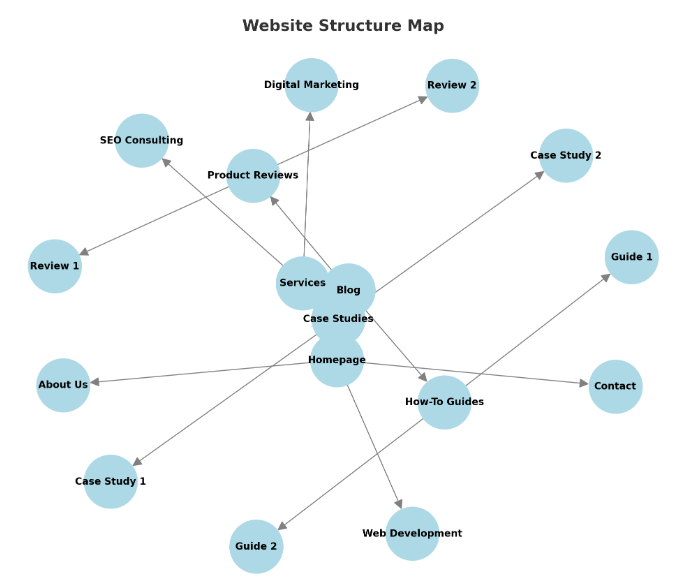
Above is a picture of what website content organization structure might look like. You can see it contains a lot of elements such as Home, About, Services etc, and sub sections flow out from these inner pages. How the content of a website is organized can vary from niche to niche and all depends on your reason for having the website. Keep this visual in mind as you read through the rest of this guidance
Step 1: Define Your Goals and Audience
a) Set Clear Objectives
- What do you want your website to achieve? Define specific goals, such as driving sales, sharing knowledge, or building a community.
- Prioritize your goals to align content structure with primary objectives.
b) Understand Your Audience
- Create user personas to understand your audience’s preferences, challenges, and browsing behaviors.
- Use tools like Google Analytics to analyze existing user behavior for informed decisions.
Step 2: Conduct a Content Inventory
a) Audit Existing Content
If you’re organizing an existing site, start with a content audit:
- List all pages and categorize their purpose (e.g., informational, transactional, or navigational).
- Identify outdated, redundant, or underperforming content.
b) Use Tools for Efficiency
- Screaming Frog: Crawls your site to map out content.
- Google Search Console: Identifies high-performing pages and areas for improvement.
c) Group Related Content
Organize pages into logical groups based on topics or themes. For example:
- Blog posts could be categorized under “How-To Guides,” “Product Reviews,” or “Case Studies.”
Step 3: Plan a Logical Site Structure
a) Implement a Hierarchical Structure
A clear hierarchy helps users and search engines understand your content:
- Homepage: Acts as the central hub.
- Main Categories: Broad topics relevant to your site’s goals (e.g., “Services,” “Blog”).
- Subcategories: More specific topics under each main category.
- Individual Pages: Detailed content that supports subcategories.
b) Use Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumbs show users where they are within your site’s hierarchy, making navigation easier.
Step 4: Optimize Your Navigation Menu
a) Simplify Your Menu
- Limit options to avoid overwhelming users. Keep the menu concise, with 5-7 primary links.
- Use intuitive labels like “About Us,” “Contact,” or “Shop.”
b) Include a Search Function
For larger websites, a search bar is invaluable for helping users find content quickly.
Step 5: Create a Content Calendar
Organizing web content extends beyond structure—timely updates and new content are key:
- Plan Topics in Advance: Use keyword research tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to identify trending topics.
- Schedule Posts: Maintain consistency by scheduling updates on a weekly or monthly basis.
Step 6: Write for Both Users and Search Engines
a) Prioritize Readability
- Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and headings for easy scanning.
- Adopt a conversational tone where appropriate.
b) Incorporate Keywords Strategically
- Avoid keyword stuffing. Focus on natural integration into headings, subheadings, and meta descriptions.
c) Add Metadata
- Optimize title tags and meta descriptions for SEO and user clarity.
- Example: For a page on “Best Hiking Gear,” use a title like “Top 10 Hiking Essentials for Every Adventurer.”
Step 7: Design Content for Accessibility
a) Use Descriptive Headings
Clear headings (H1, H2, H3) allow screen readers and search engines to interpret your content accurately.
b) Add Alt Text to Images
Ensure all images include descriptive alt text for accessibility and SEO benefits.
c) Choose High-Contrast Design
Select font colors and backgrounds that are easy to read for all users.
Step 8: Leverage Internal Linking
Internal links guide users through your site while improving SEO by:
- Distributing page authority.
- Helping search engines understand your content’s relationships.
For example, link a blog post about “Digital Marketing Trends” to your service page for “SEO Consulting.”
Step 9: Test Your Website Structure
a) Use Heatmaps
Tools like Hotjar show how users navigate your site, revealing areas for improvement.
b) Perform User Testing
Invite users to complete specific tasks and provide feedback on ease of navigation.
c) Check for Broken Links
Use tools like Broken Link Checker to identify and fix dead links.
Step 10: Maintain and Update Content
a) Regularly Review Performance
- Analyze metrics like bounce rate, time on page, and conversion rates.
- Use A/B testing to refine layouts or calls-to-action.
b) Archive or Refresh Old Content
- Archive outdated pages to declutter your site.
- Update high-performing pages to keep them relevant and competitive.
Pro Tips for Advanced Users
- Create Topic Clusters: Use pillar content linked to related subtopics to enhance SEO and user experience.
- Implement Schema Markup: Add structured data for better SERP visibility.
- Dynamic Content Management: Use CMS platforms like WordPress or Drupal to organize and automate updates.
Tools to Streamline Web Content Organization
- CMS Platforms: WordPress, Joomla, Squarespace.
- SEO Tools: Yoast SEO, Screaming Frog, SEMrush.
- Analytics Tools: Google Analytics, Hotjar.
- Accessibility Tools: WAVE, axe DevTools.